Sources of Fibres and their Classification:
There are many different sources from which we can obtain fibres and therefore, weclassify them accordingly.
i) Fibres from Natural Sources: All the fibres obtained from nature, i.e., plants
or animals, are known as natural fibres. e.g. cotton, wool, linen, silk, etc. Fibres
obtained from plant source are called cellulosic fibre e.g., cotton and linen. The
fibres that come from animal sources are also known as protein fibres, e.g.,
wool and silk.
Sources of commonly used natural fibres are shown below in Fig.
Figure:Sources of natural fibres – Cotton, Wool and Silk
ii) Man-Made fibres: The fibres which are made in laboratories using chemicals
are known as man-made fibres and these are of following two types:
a) Regenerated fibres – These fibres are made from extremely small cotton
fibres or any other fibre source such as wood pulp, milk protein, etc.
Chemicals are used to dissolve these and the solution is then converted into
solid fibres. Examples are rayon (cellulose out of viscose/acetate/triacetate)
of different types, casein fibre (from milk) and soya bean fibre.
b) Synthetic fibres - These are made using various petrochemical products.
Nylon, acrylic and polyester are all synthetic fibres.
It is advisable to use garments made of natural fibres which are eco-friendly in nature.
Sometimes synthetic fibres may cause allergies if worn next to skin. Sources of
commonly used natural and man made fibres are presented in Table.
Figure:Commonly used natural and man-made fibres
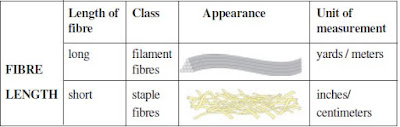
Classification according to the Length of Fibres :
The fibres we have listed above are short or long. The short length fibres are calledstaple fibres and are measured in inches or centimeters, e.g., cotton, wool and linen.
The long fibres are known as filaments and are measured in yards / meters, e.g., silk
and all man-made fibres.
Figure:Classification according to the Length of Fibres









1 Comments
I have opened a textile blog named Textile Definition, your source for up-to-date information on the latest textile technologies. Here you will find an extensive library of resources, including articles, videos, and tutorials about the various aspects of the textile industry. We strive to provide our readers with the most accurate and up-to-date information to ensure that they can make informed decisions about their textile needs. Whether you are looking for the newest textile materials, the most efficient manufacturing processes, or the best way to care for your textiles, you can find it all here. I invite you to visiting and happy reading my blog!
ReplyDelete